44 egg structure with labels
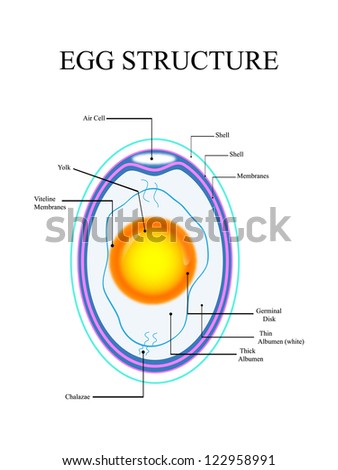
Science of Eggs: Anatomy of an Egg | Exploratorium An air space forms when the contents of the egg cool and contract after the egg is laid. The air cell usually rests between the outer and inner membranes at the egg's larger end, and it accounts for the crater you often see at the end of a hard-cooked egg. The air cell grows larger as an egg ages. The egg white is known as the albumen, which ... Solved The structure indicated by Labels A and B are - Chegg The structure indicated by Labels A and B are responsible for: Production of ADH and oxytocin that are released into the anterior pituitary Production of FSH and LH that are released into the interior pituitary Production of FSH and tell that are released into the posterio pintar Production of ADH and oxytocin that are released to the posterior ...
Chicken egg structure ( in simple way) - YouTube In this video I have explained about chicken egg structure in a simple way.. Thank uhttps:// ...

Egg structure with labels
Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Science of Cooking Eggshell The outer eggshell is made almost entirely of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and is covered with as many as 17,000 tiny pores. It is a semipermeable membrane, which allows air and moisture to pass through its pores. The shell also has a thin outermost coating called the bloom or cuticle that helps keep out bacteria and dust (see below 15). 2. My Account | Ulrick & Short We have over 20 years of food industry knowledge and expertise in clean label ingredient development. We work with manufacturers like you to overcome the most difficult product formulation challenges from reducing fat and sugar, replacing egg and removing phosphates to improving product stability, texture and appearance. What Do the Labels on Egg Cartons Actually Mean - Lifehacker If you want more information, Whole Foods' eggs use a series of labels that describe where laying hens live - Cage Free Plus, Outdoor Access, Pasture Raised, Mobile Houses on Pasture. Large, extra...
Egg structure with labels. PDF Egg Parts - University of Illinois Extension Egg Parts Color each part of the egg a different colorand label each part of the egg. yolkshell vitelline membrane germinal discmembranesalbumen Use each word only once: air cellgerminal discvitelline membrane albumen or whitemembranesyolk chalazashell label parts of a cell yolk is surruondedby the substance called - Science - Cell - Structure we have 9 Images about yolk is surruondedby the substance called - Science - Cell - Structure like Parts and Function of Digestive System for Med School & Nursing, 2.4.1 Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes - YouTube and also Connective tissue - BIOLOGY4ISC. Import & Export Library | Food Safety and Inspection Service Eligible Egg Products, Raw and Processed Beef, Raw and Processed Chicken, Raw and Processed Duck, Raw and Processed Emu, Raw and Processed Goat, Raw and Processed Goose, Raw and Processed Guinea, Raw and Processed Ostrich, Raw and Processed Pork, Raw and Processed Rhea, Raw and Processed Sheep (Lamb), Raw and Processed Squab, Raw and Processed Turkey, Raw and Processed Veal Structure of the Egg - Incubation and Embryology - University of ... Structure of the Egg The egg is a biological structure intended by nature for reproduction. It protects and provides a complete diet for the developing embryo, and serves as the principal source of food for the first few days of the chick's life. The egg is also one of the most nutritious and versatile of human foods.
Physical Structure and Composition of an Egg - Prezi Physical Structure and Composition of an Egg Air Cell This is the empty space between the white and shell at the large end of the egg which is barely existent in newly laid egg. Albumen/Egg White. Chalaza This is the ropey strands of egg white at both sides of the egg, which anchor the yolk in place in the center of the thick white. The Parts of the Egg - Virginia Tech In a fresh egg, we can see white cords attached to the yolk sac. These two cords, called chalazae, are made of twisted strands of mucin fibers that are a special form of protein. The chalazae hold the yolk in the center of the egg. The yolk is the source of food for the embryo and contains all the fat in the egg. Structure of The Egg - DAVA Foods An egg from a hen consists of approximately 2/3 egg white and 1/3 egg yolk. Bacterial retardant The egg white protects the yolk, be it among other reasons because of the enzyme lysozyme, which splits the beta- (1,4)-glycoside bond in the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria, wherin the bacterial cell is destroyed. Lateral flow assays: Principles, designs and labels ... Sep 01, 2016 · From that time on, it has been widely used in detecting various molecules, such as cancer markers, microorganisms, mycotoxins, heavy metals, and pesticides. In this study, the principles of lateral flow assay, its structure, labels that are used in the construction of LFA and developed LFAs in literature are summarized. 2.
Structure of the egg - HEDEGAARD - DAVA The structure of the egg An egg basically consists of three parts: a shell an egg white an egg yolk An egg from a hen consists of approximately 2/3 egg white and 1/3 egg yolk. The eggshell The shell is built of 8-10,000 pores, which ensures that oxygen can penetrate and CO 2 and other gases can escape. Label Chicken Egg (#1) Printout - EnchantedLearning.com Label the Chicken Egg (#1) Label the cross section of a newly-laid chicken egg. Chickens Bird Printouts air cell - an empty space located at the large end of the egg; it is between the inner and outer shell membranes. chalaza - a spiral, rope-like strand that anchors the yolk in the thick egg white. The Human Egg Cell | Egg Donation | Altrui The human egg, or ovum, is one of the largest cells in the human body. That said, it is still very small and measures approximately 0.12 mm in diameter. You would need 9 eggs to reach a millimetre in length, and if you laid 100 of them side by side they would sit on a line just 12 mm (1.2cm) long. How are eggs produced? The Anatomy of an Egg: We Take a Closer Look - Hobby Farms You might be familiar with the chalazae, just in a different context: As an egg is cracked open, the two cords snap back toward the yolk and appear as small knots or strings on the surface of the egg's contents. The Shell The shell's main function is maintaining the integrity of the egg's yolk and albumen and protecting the developing embryo.
The Different Parts of an Egg | Sauder's Eggs Together, egg white fluid consists of four segmented layers, with each alternating between a thin and thick consistency. This mix of consistencies provides egg whites the robust template that holds over 40 different amino acids — and is precisely what gives egg whites their well-known protein-packed reputation. Chalaziferous White.
Recalls & Public Health Alerts | Food Safety and Inspection ... WASHINGTON, Aug. 31, 2022 – Valrhona Inc., a Brooklyn, New York establishment, is recalling approximately 66 pounds of dried albumin egg products, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) announced today. The products were produced in Italy, a country ineligible to...
The Structure of the Egg. Ovum Anatomy. Vector ... - Dreamstime Illustration about The structure of the egg. Ovum anatomy. Vector illustration on isolated background. Illustration of anatomy, cell, eps10 - 195448433
How Do Chickens Make Eggs? - Australian Eggs How Is an Egg Formed? A laying hen’s ovary holds thousands of tiny ova, or future egg yolks. Birds are unique among animals because only one ovary (the left) matures to the stage where it releases eggs. When a yolk is ready, it moves out of the ovary and into the oviduct - a tube-like structure that is divided into different sections.
Egg structure. Anatomy of a birds egg, labeled chart with names ... - Alamy Download this stock image: Egg structure. Anatomy of a birds egg, labeled chart with names of the components - diagram illustration on white background. - 2C46TCD from Alamy's library of millions of high resolution stock photos, illustrations and vectors.
Aeration/Foaming/Structure - American Egg Board Aeration can be achieved in several ways including biological (yeast), chemical (baking soda), mechanical (methods of mixing certain ingredients or the batter through whipping or beating), physical (lamination or steam), or a combination of those methods. Each is designed to introduce a gas, such as air, into a liquid or viscous solution. 1.
Oliver’s Labels Cute, colorful and ultra durable personalized labels and tags. Oliver’s Labels ... Personalized Easter Egg; Easter Lamb Decals ... Add some structure into your ...
Egg Allergy | Allergy UK | National Charity Egg free diet information: Labelling Reading a food Label. In the European Union (EU) ingredients lists on food labels must clearly emphasise (for example in bold or highlighted) whether they contain any of the 14 most common allergens. One of these 14 foods that must be labelled is EGG
The Anatomy of a Chicken Egg - Parts and Functions of an Egg As the egg continues to age, moisture and carbon dioxide leave through the pores and air enters to replace them. Chalazae Chalazae are dark spiral ropes of egg white. They hold the yolk in place at the center of the egg. It is important to note that fresh eggs have more conspicuous chalazae. The albumen
Structure of the Amniotic Egg - Memorial University of Newfoundland Structure of the Amniotic Egg. Evolution of eggs with a water-impermeable amniotic membrane surrounding a fluid-filled amniotic cavity permits embryonic development on land without danger of dessication. The main diagram shows the arrangement of membranes in a typical egg-laying oviparous vertebrates. In live-bearing viviparous vertebrates, the shell and chorionic membrane are absent and the ...
Egg Replacement | Ulrick & Short Structure Control ; Ingredients ; Derived from one of the largest ranges of functional crop bases available, all of our ingredients are clean label, non-GM and plant-based. ... Ulrick & Short has developed a range of functional, clean label egg replacements to offer partial or total egg replacement. ovaprox is available in both dry or liquid ...
Egg: Definition, Structure and Classification - Your Article Library Science defines egg as a cell from which a living organism takes birth and grows. All animals (including birds) lay eggs, except mammals which give birth to babies. An egg laying animal lays eggs, no matter whether they are fertilized or not. In other words, it does not have to be mated to lay an egg.
Solved In the sketch of the structure of NF3 label all | Chegg.com In the sketch of the structure of NF3 label all bonds. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help o: N(p) - F(p) T: N(P) - F(p) 11 O: N(P) - F(sp) T. : N(spl) - F(p) Lone pair in p orbital Lone pair in sp orbital Lone pair in 8 orbital a : N(sp) - F(p)
Packaging, Labeling, Transporting, Storing — Food Law Labeling egg products-- FDA and USDA share labeling authority; 9 CFR 590.411 and 9 CFR 590.680. Have the Labeling Requirements been Met? Label Approval FDA does not pre-approve labels; FDA may offer suggestions if the processor inquires; FDA will enforce law after the label is put in use.
Egg Nutrition Facts - American Egg Board The Nutrition Facts label for packaged foods helps people make more informed food choices. These labels provide information about the calories and nutrients in different sizes of eggs. The % Daily Value (DV) tells you how much a nutrient in a serving of food contributes to a daily diet. The Nutrition Facts Panel formats are for consumer use only.
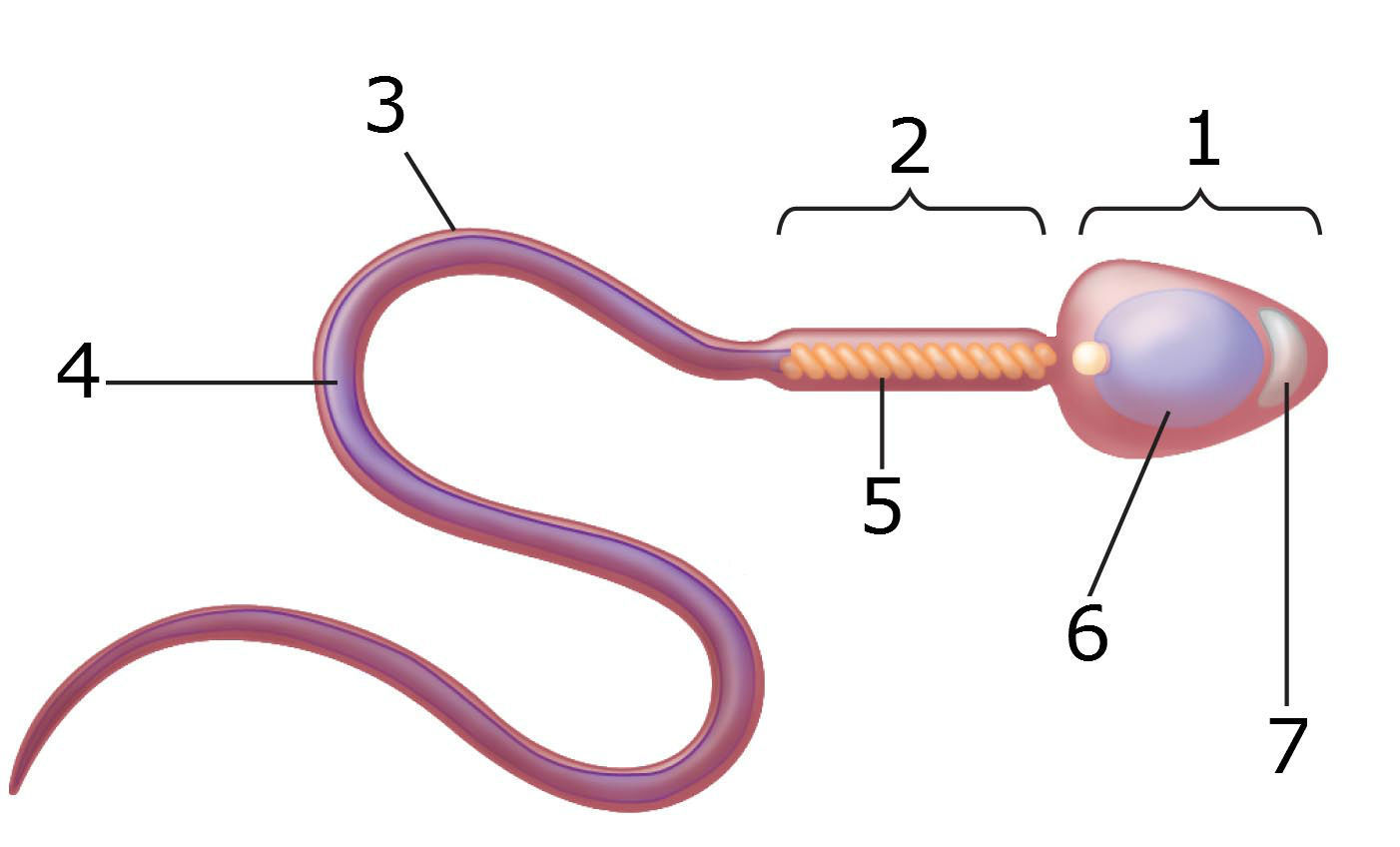
Structure of the Gametes - Developmental Biology - NCBI Bookshelf Structure of the Gametes. A complex dialogue exists between egg and sperm. The egg activates the sperm metabolism that is essential for fertilization, and the sperm reciprocates by activating the egg metabolism needed for the onset of development. But before we investigate these aspects of fertilization, we need to consider the structures of ...
Types of Eggs - The Spruce Eats Here are some of the most common. Fried eggs (which includes styles like over-easy and sunny side up) Scrambled eggs. Poached eggs. Boiled eggs ( hard-boiled and soft-boiled) Shirred or baked eggs. Frittatas and omelets. Eggs are also used in emulsified sauces like mayonnaise, Hollandaise and others.
What Do the Labels on Egg Cartons Actually Mean - Lifehacker If you want more information, Whole Foods' eggs use a series of labels that describe where laying hens live - Cage Free Plus, Outdoor Access, Pasture Raised, Mobile Houses on Pasture. Large, extra...










Post a Comment for "44 egg structure with labels"